
Commercial Kitchen Fire Suppression Systems: The Ultimate Guide
A commercial kitchen fire suppression system is your automated, built-in firefighter. It’s a network of components engineered to instantly detect and knock down a fire right where it starts in a high-heat cooking environment. Think of it as the ultimate guardian for your kitchen—a "firefighter in a box" that’s always on duty, ready to spring into action to protect your people, your property, and your entire business.
Why Your Kitchen Needs an Unseen Guardian

Picture a busy dinner service. You've got high heat, sizzling grease, and a team in constant motion. That incredible energy is what makes a restaurant successful, but it also creates the perfect storm for a fire. A simple flare-up can escalate into a full-blown disaster in the blink of an eye.
This is precisely why commercial kitchen fire suppression systems are non-negotiable. They aren't just another piece of equipment; they're a fundamental investment in the safety and continuity of your business. A fire can trigger catastrophic financial losses, do irreparable harm to your hard-earned reputation, and—most importantly—cause serious injuries.
More Than Just Ticking a Box
Sure, meeting fire codes is a must, but the true value of these systems goes way beyond passing an inspection. They give you an automated, 24/7 defense that reacts faster than any human possibly could. That rapid response is everything. It can smother a fire at its source, often before anyone even realizes there's a problem.
Installing a professional system provides incredible peace of mind and shows a deep commitment to the well-being of your staff and guests. It's a cornerstone of any responsible foodservice operation.
A Growing Market Shows a Critical Need
The sheer importance of these systems is mirrored in their market growth. The global demand for commercial kitchen fire suppression systems has pushed the market to a valuation of around USD 1.2 billion as of 2024. Projections show this figure more than doubling to USD 2.5 billion by 2033, a surge driven by a greater awareness of fire hazards in the food industry. You can discover more insights about the market's strong growth trajectory on verifiedmarketreports.com.
A fire suppression system isn’t an expense; it’s an insurance policy against the single greatest threat to your restaurant's survival. It protects your investment, your people, and your ability to open for business tomorrow.
Getting a handle on how this technology works is the first step toward properly safeguarding your establishment. Once you understand its role, you'll see why making the right choice on system type, installation, and maintenance is so critical for every operator.
How a Fire Suppression System Actually Works
A commercial kitchen fire suppression system is like having a highly trained, automated firefighter on standby 24/7. The moment a fire erupts, it jumps into action, following a precise, pre-engineered sequence that moves from detection to extinguishment in just a few seconds. This isn't magic; it's a meticulously designed cause-and-effect chain that protects your kitchen when every second is critical.
To really get how it works, let’s imagine a classic kitchen nightmare: a grease fire flares up on the range during a chaotic dinner rush. The heat is intensifying fast, creating a seriously dangerous situation. This is where the system’s first crucial step kicks in.
Step 1: Detection of the Fire
Every commercial kitchen fire suppression system is armed with heat detectors, and the most common type you’ll see are fusible links. These are small, temperature-sensitive metal parts placed strategically in the exhaust hood, right above the cooking appliances. Each link is engineered to separate—or "fuse"—at a very specific, predetermined temperature.
Think of a fusible link as a heat-activated tripwire. In our scenario, as that grease fire roars to life, the hot air and radiant heat shoot straight up into the exhaust hood. Once the temperature at the fusible link hits its trigger point—usually somewhere between 360°F and 500°F—the link melts and breaks apart.
Step 2: Activation of the System
The second a fusible link separates, it instantly releases the tension on a connected detection cable. This triggers the system's mechanical control head, which is essentially the brain of the whole operation. The activation is immediate and sets off a rapid chain reaction.
Once triggered, the control head does two critical things almost at the same time. First, it punctures a cartridge of pressurized gas (like nitrogen), which then forces the fire-suppressing agent out of its storage tank and through a network of pipes. Second, it flips a switch to cut the fuel supply to the appliances.
Step 3: Suppression of the Flames
With the system now fully activated, the wet chemical suppressant travels through the piping and is blasted out through nozzles aimed directly at the cooking appliances and up into the exhaust plenum. These nozzles are carefully positioned during installation to make sure every inch of the hazard area is completely covered.
This wet chemical agent is a specialized liquid designed specifically for grease fires. When it sprays onto the fire, it performs two vital jobs:
- Flame Knockdown: The agent quickly smothers the flames on contact.
- Saponification: It chemically reacts with the hot cooking grease and oils, creating a thick, soapy foam blanket over the entire surface. This blanket starves the fire of oxygen and stops flammable vapors from escaping.
That saponification process is exactly why you never use water on a grease fire—water can cause a violent, explosive reaction. The wet chemical agent, however, safely contains and extinguishes it.
The dual action of smothering the fire and chemically altering the fuel source is what makes wet chemical agents so remarkably effective. This process not only puts the fire out but also provides a cooling effect to prevent it from reigniting.
Step 4: Shutdown of Fuel Sources
While the wet chemical agent is being discharged, the system is also automatically shutting down the energy sources to the connected appliances. If you've got a gas range, a valve will instantly snap the gas line shut. For electric appliances, the system will trip a circuit breaker, cutting all the power.
This final step is absolutely crucial. By killing the heat source, the system ensures the fire can’t just reignite after the initial flames are knocked down. This perfectly coordinated, four-step sequence provides a powerful defense against the unique dangers of a commercial kitchen fire.
The infographic below helps visualize the key installation process that enables this life-saving sequence.
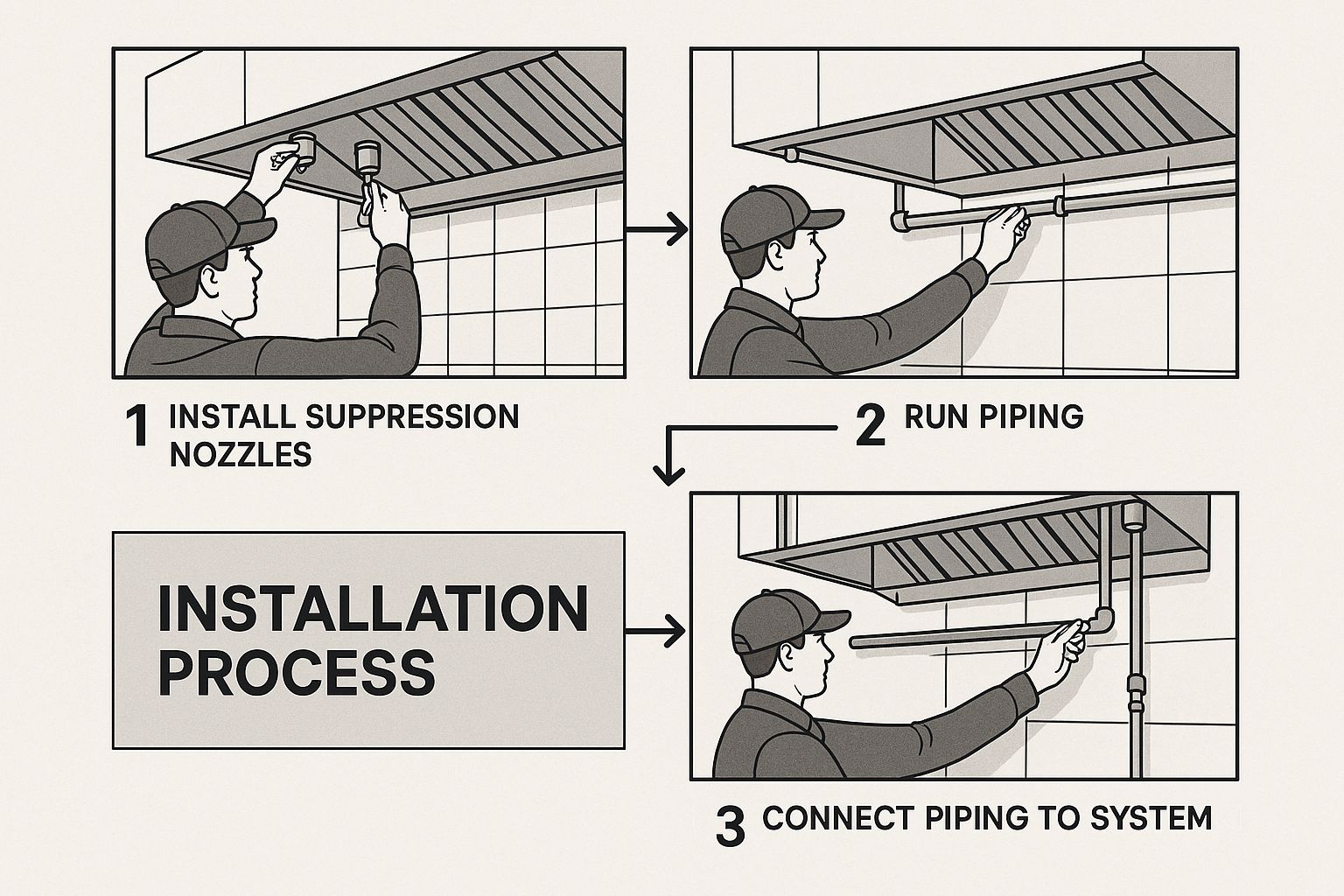
This image highlights how professional installation by a certified technician is essential for ensuring every component, from detectors to nozzles, is placed correctly to guarantee effective operation during an emergency.
Choosing the Right Type of Suppression System

Picking out a fire suppression system for your commercial kitchen isn't like choosing a new oven. It’s a specialized decision, one that’s rooted in the very real and unique fire risks that come with a professional cooking environment. Not all systems are built the same, and the right choice boils down to the specific hazards you're up against.
For just about every modern restaurant, there’s one clear winner that has become the undisputed champ of kitchen safety.
The overwhelming industry standard is the Wet Chemical System. These systems are specifically engineered to handle the intense fires that can erupt from hot cooking oils and grease—a constant threat in any busy kitchen. The demand for this kind of targeted protection has exploded, showing just how critical this technology has become.
The market for this kind of industrial fire protection was valued at USD 35.56 billion back in 2020 and is expected to nearly double, hitting an estimated USD 68.46 billion by 2030. That's a massive jump, and it highlights a serious industry-wide commitment to better fire safety. You can learn more about these market projections on internationalfireandsafetyjournal.com.
Why Wet Chemical Systems Dominate
The real genius of a wet chemical system is its two-pronged attack on a grease fire. When the system kicks on, it sprays a liquid agent—usually a solution based on potassium carbonate—directly over the burning appliance. This spray does two crucial things at once.
First, it smothers the fire, robbing it of the oxygen it needs to burn. But the second part is the real magic: it kicks off a chemical reaction called saponification.
Saponification Explained
Think of it like an emergency soap-making process happening right on your cooktop. The wet chemical agent reacts with the hot grease and oils, turning them into a thick, soapy foam. This foam blanket is the key—it doesn't just smother the flames, it also cools the surface down, which is vital for preventing a dangerous reignition.
This one-two punch of cooling and smothering is what makes wet chemical systems so incredibly effective against Class K fires, the specific classification for fires involving cooking media.
Dry Chemical Systems: The Old-School Approach
Before wet chemical systems became the standard, Dry Chemical Systems were much more common. These use a fine powder, like sodium bicarbonate, to knock down flames. While they can put a fire out, they come with some serious downsides in a kitchen.
- No Cooling Effect: Dry chemicals smother the fire but do nothing to cool the superheated grease. This creates a huge risk of the fire flaring right back up.
- A Nightmare to Clean: That fine powder is corrosive and gets absolutely everywhere. The cleanup is extensive, costly, and can shut your kitchen down for a long time.
- Contamination City: The powder can infiltrate every nook and cranny, contaminating food supplies and wrecking sensitive electronic equipment.
Because of these major drawbacks, you'll rarely see dry chemical systems being installed to protect cooking appliances anymore, though they still have a place in other industrial settings.
Other Specialized System Types
To give you a full picture, it helps to know what else is out there. While wet chemical systems are the go-to for the cooking line, a few other systems exist for different, more specialized commercial kitchen fire suppression system applications.
For a clearer comparison, let's break down the common system types, what they use, and where they shine.
Comparison of Kitchen Fire Suppression System Types
| System Type | Suppressant Agent | Primary Application | Key Advantage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Wet Chemical | Potassium Carbonate Solution | Cooking Appliances (Fryers, Grills) | Cools and smothers grease fires, preventing reignition. |
| Dry Chemical | Sodium Bicarbonate Powder | General Industrial Fires | Knocks down flames quickly. |
| Carbon Dioxide (CO2) | Carbon Dioxide Gas | Areas with Sensitive Electronics | Leaves no residue, safe for electronics. |
| Water Mist | Fine Water Droplets | High-End or Specialized Kitchens | Eco-friendly and minimizes water damage. |
As you can see, each system has a very specific job.
Carbon Dioxide (CO2) Systems are great for places with sensitive electronics because the gas displaces oxygen without leaving any residue. But they’re a bad fit for open cooking areas because the gas dissipates too quickly and creates a suffocation risk for your staff.
Water Mist Systems are an interesting, eco-friendly option. They use incredibly fine water droplets to cool the fire and displace oxygen. They are generally more complex and costly, often reserved for unique, high-end applications where even the slightest water damage is a major concern.
For any restaurant owner, understanding these differences is key. But when you sit down with a fire protection professional, the conversation will almost always circle back to a wet chemical system. It's simply the safest, most effective, and code-compliant choice for protecting the heart of your operation: the cooking line.
Navigating Critical NFPA Codes and Compliance
Fire codes aren't just bureaucratic red tape; they're a playbook for safety, written from decades of real-world experience and, unfortunately, lessons learned from real fires. For anyone running a commercial kitchen, understanding these rules is fundamental to protecting your business, your team, and your customers.
This isn't about memorizing code numbers. It's about grasping the practical requirements that keep your establishment safe and legally sound. When it comes to commercial kitchen fire suppression systems, there are two crucial documents from the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) you need to know. These aren't suggestions—they're the standards your local fire marshal enforces, and they dictate just about every part of your kitchen's fire safety plan.
The Two Pillars of Kitchen Fire Safety
Think of these standards as the twin pillars holding up your entire fire protection strategy. Each one governs a distinct but interconnected part of your kitchen's ecosystem.
- NFPA 96: Standard for Ventilation Control and Fire Protection of Commercial Cooking Operations: This is the big one. It covers the whole commercial cooking setup, from the construction of your exhaust hood and ductwork all the way to your mandatory cleaning schedules. A key piece of NFPA 96 is the rule that every commercial kitchen must have an approved fire suppression system installed.
- NFPA 17A: Standard for Wet Chemical Extinguishing Systems: This standard zooms in on the fire suppression system itself. It lays out the specific rules for the design, installation, testing, and maintenance of the wet chemical systems that have become the industry standard for protecting modern cooking appliances.
Together, these two documents create a comprehensive safety net. NFPA 96 makes sure your kitchen's ventilation is built to contain a fire, while NFPA 17A ensures your suppression system is ready to knock it out. Properly managing your ventilation is a critical first step; in fact, you can dive deeper into those requirements in our guide to commercial kitchen ventilation requirements. This knowledge helps ensure your entire setup works together seamlessly.
The Mandatory Six-Month Inspection
One of the most critical mandates from the NFPA is the requirement for a professional inspection and servicing of your fire suppression system every six months. This is a non-negotiable legal requirement.
During this semi-annual service, a licensed fire protection technician will perform a detailed examination to certify that your system is in perfect working order.
A passed inspection isn't just a piece of paper. It's certified proof that your first line of defense against a catastrophic fire is ready to perform flawlessly at a moment's notice.
So, what actually happens during this crucial service? A certified technician will:
- Check the Fusible Links: They'll verify the heat-detecting links haven't been damaged or painted over and replace any showing signs of wear or that have hit their expiration date.
- Test the Detection Line: The tech will operate the detection line to ensure the activation mechanism in the control head works smoothly and without any obstruction.
- Inspect Nozzles: Every single nozzle is checked to ensure it's aimed correctly, free of grease buildup, and has its protective cap in place. Clogged nozzles are a primary cause of system failure.
- Verify Agent Tanks: The pressure and volume of the wet chemical agent in the storage cylinders are checked to confirm they fall within the manufacturer's specified limits.
- Test the Fuel Shutoff: The technician will confirm that the system correctly and automatically shuts off the gas or electrical supply to the cooking appliances when activated.
- Document and Certify: Finally, they will document the entire inspection, update the system's service tag with the date, and provide you with a detailed report for your records and the fire marshal.
Your Responsibilities Beyond the Inspection
While the professional technician handles the semi-annual service, compliance is a year-round job for you. As a kitchen owner or manager, you're required to ensure staff are trained on the system's location and how to use the manual pull station.
You must also maintain clear access to that pull station at all times—it can't be blocked by equipment or supplies. Furthermore, it's your duty to keep the system's components, especially the nozzles under the hood, clean from the daily grease accumulation that's just part of life in a kitchen. Fostering a culture of safety and awareness turns compliance from a chore into a powerful, proactive strategy for protecting your entire operation.
The Vital Role of Your Kitchen Hood System
Most people glance at a commercial kitchen hood and just see a big, noisy vent. But in the world of fire safety, it’s the command center for your entire fire protection strategy. Your exhaust hood and your commercial kitchen fire suppression systems have a critical partnership, forming the frontline defense right where the danger is highest.
Think of your kitchen hood as the first responder already on the scene. Every bit of heat, smoke, and grease-filled vapor from your cooking appliances gets funneled directly into this one spot. By weaving detectors, nozzles, and piping right into the hood and its ductwork, the system is perfectly positioned to attack a fire at its most likely starting point. This means you get an immediate and targeted response.
The Hood as Command Central for Fire Defense
This setup is no accident. Fires in a commercial kitchen almost always spark on a cooking surface and then climb upward into the plenum and ductwork, feeding on all that built-up grease. Placing the fire suppression components inside the hood system means the defense is already in position before a fire even has a chance to start.
It's a seamless system where every part has a job:
- Heat Detectors: These are fusible links placed right in the path of rising heat, guaranteeing the quickest possible detection of a dangerous temperature spike.
- Discharge Nozzles: They're angled with precision to cover specific appliances and the exhaust opening, making sure the wet chemical agent blankets the entire hazard zone.
- Piping Network: Tucked away inside the hood, this network is the delivery system, ready to send the fire-suppressing agent instantly when triggered.
This integrated design is a huge reason the market for kitchen hood fire suppression systems keeps growing. It’s projected to hit nearly USD 968.1 million by 2031, a trend pushed by strict safety standards that recognize the hood as the critical control point. For a closer look at the market, you can review the full research on kitchen hood fire suppression systems at metastatinsight.com.
Why Hood Cleaning Is a Critical Fire Prevention Task
An automated system is a powerful tool, but it can’t work effectively if it’s caked in grease. This is why regular, professional cleaning of your kitchen hood isn't just about sanitation—it's one of the most vital fire prevention tasks you can perform. Layers of grease are just highly flammable fuel waiting for a spark.
If your fire suppression system is the firefighter, a clean hood is the fireproof uniform it wears. A grease-caked hood gives a fire a direct highway to spread, which can overwhelm even the best-designed system.
Skipping hood cleanings completely undermines your multi-thousand-dollar investment in safety. Clogged filters choke off airflow and cause heat to build up, while greasy surfaces allow flames to race into the ductwork. Once a fire gets in there, it becomes much harder and more dangerous to extinguish. To make sure your entire ventilation system is working properly, it’s worth reviewing a complete commercial kitchen exhaust hood guide, which reinforces this crucial link between cleanliness and safety. A clean hood lets your suppression system do its job, isolating and killing a fire before it turns into a catastrophe.
Essential Installation and Maintenance Practices
A commercial kitchen fire suppression system is an incredible piece of engineering, but it’s absolutely not a "set it and forget it" device. Its reliability hangs on two things: a flawless professional installation and a consistent, disciplined maintenance routine. When you get these right, your system becomes a life-saving guardian you can truly count on.
Think of it like a high-performance car. You wouldn't let an amateur build the engine, and you definitely wouldn't skip its scheduled oil changes. The same exact logic applies here. Professional expertise at the start and diligent upkeep are non-negotiable if you want your system to perform perfectly when you need it most.
The Critical Importance of Professional Installation
Trying to DIY an installation or hiring an uncertified handyman for your fire suppression system is one of the most dangerous gambles you can take in a commercial kitchen. This isn't a simple appliance; it's a complex life-safety system. Only a licensed and certified fire protection professional has the knowledge to do the job right.
An improper installation can lead to catastrophic failure. Some of the most common mistakes include:
- Incorrect Nozzle Placement: Nozzles have to be aimed with precision to cover specific hazard zones on each piece of cooking equipment. If a nozzle is off by just a few inches, it can leave a dangerous blind spot where a fire could rage unchecked.
- Improper Calibration: The activation mechanism, from the fusible links to the tension on the detection line, must be calibrated to exact manufacturer specifications. If it's too loose, the system might not trigger. Too tight, and you risk a false discharge that shuts down your kitchen.
- Failed Fuel Shutoff Integration: A core function of the system is to automatically cut the gas or electricity to the appliances. An installer who fails to wire this correctly leaves the fuel source active, creating a massive risk of the fire reigniting.
Professional installation isn’t just a best practice—it's a legal requirement mandated by NFPA codes. A faulty setup not only puts lives at risk but will also void your insurance coverage and lead to severe fines from the fire marshal.
Building a Bulletproof Maintenance Schedule
Once your system is properly installed, the responsibility for its upkeep begins. A proactive maintenance schedule is your absolute best defense against system failure. This routine can be broken down into three essential tiers.
1. Daily and Weekly Staff Checks
Your kitchen team is the first line of defense. It's easy to integrate these simple visual checks into your daily closing procedures:
- Check Nozzle Caps: Make sure the protective caps are on all nozzles. These little caps are crucial for preventing grease from clogging the nozzle heads, which is a primary cause of system failure.
- Clear Obstructions: Ensure nothing is blocking the manual pull station or the nozzles themselves. A misplaced box or piece of equipment could render the system useless.
- Look for Damage: Do a quick visual scan for any visible damage to the piping or other components under the hood.
A clean kitchen is fundamental to fire safety. For a deeper dive into best practices that directly support your fire suppression system's effectiveness, check out these essential commercial kitchen cleaning tips.
2. Monthly In-House Inspections
Once a month, a manager should conduct a slightly more detailed check. This involves documenting that the pressure gauges on the agent tanks are in the green, verifying the service tag is up to date, and confirming that the fuel shutoffs haven't been accidentally tampered with.
3. Mandatory Semi-Annual Professional Servicing
By law, a certified technician must service your system every six months. This is a comprehensive, hands-on inspection. They will test the activation mechanisms, verify agent levels, replace fusible links on schedule, and provide the official certification tag that keeps you compliant. This professional service is the ultimate verification that your system is ready for an emergency.
Got Questions? We’ve Got Answers.
When it comes to commercial kitchen fire suppression systems, a lot of questions can pop up. It's a critical piece of safety equipment, and knowing the ins and outs is part of running a smart, safe kitchen. Here are some straightforward answers to the questions we hear most often from restaurant owners.
How Often Does My Kitchen Fire Suppression System Need to Be Inspected?
Think of it like a regular health check-up for your kitchen's most important safety feature. According to NFPA 96, your system needs a professional inspection and service by a certified technician every six months. This isn't just a suggestion—it's a legal requirement that ensures every single component is ready to go when you need it most.
During these semi-annual visits, the technician goes through a detailed checklist, verifying everything from the suppressant agent levels to the mechanical parts. In between those professional services, your own team should do a quick visual check once a month. Just look for obvious red flags like heavy grease buildup on the nozzles or any visible damage.
What Happens After a Fire Suppression System Activates?
The moment your system kicks on, a few things happen almost instantly. The wet chemical agent sprays out to knock down the flames, and at the same time, the system automatically cuts the fuel or power supply to all the cooking appliances it’s connected to.
Crucial Takeaway: After a discharge, your kitchen is officially out of commission. You absolutely cannot resume cooking until the affected area is cleaned and the system has been professionally recharged with a new agent and reset by a certified fire protection company.
Can I Install a Fire Suppression System Myself?
In a word: no. You should never, ever try to install a commercial kitchen fire suppression system yourself. This isn't a DIY project; it's a complex life-safety system that demands a deep understanding of fire codes, precise component placement, and careful mechanical calibration.
Installation has to be done by a licensed and certified fire protection professional. A botched installation can lead to a catastrophic failure during a fire, will likely void your insurance policy, and can land you with hefty fines and legal trouble from your local fire marshal. It's a massive risk that's just not worth taking.
What Is the Difference Between a Wet and Dry Chemical System?
The biggest difference is in how they fight a fire and what they leave behind. A wet chemical system is the modern standard for good reason. It uses a liquid agent that, when it hits hot grease, creates a soapy, foam-like blanket. This process, called saponification, does two things at once: it smothers the fire and cools the surface to keep it from re-igniting.
A dry chemical system, on the other hand, uses a powder to smother the flames but offers zero cooling effect. This creates a huge risk of the fire flaring right back up. That powder is also corrosive and a nightmare to clean, often causing extended downtime and serious damage to your equipment. This is exactly why wet chemical systems are the superior—and required—choice for protecting modern cooking appliances.
Equipping your kitchen with the right tools is the first step toward safety and efficiency. At The Restaurant Warehouse, we provide a full range of commercial-grade equipment to build the foundation of a successful and compliant foodservice operation. Explore our extensive catalog and find the perfect solutions for your business today!
About The Author

Sean Kearney
Sean Kearney is the Founder of The Restaurant Warehouse, with 15 years of experience in the restaurant equipment industry and more than 30 years in ecommerce, beginning with Amazon.com. As an equipment distributor and supplier, Sean helps restaurant owners make confident purchasing decisions through clear pricing, practical guidance, and a more transparent online buying experience.
Connect with Sean on LinkedIn, Instagram, YouTube, or Facebook.

Leave a comment